The Forex or foreign exchange market is a global capital markets where individuals or corporations, exchange one currency for another in an effort to either generate income or hedge risk. Global volume is more than 5-trillion dollars a day and the market is open around the clock, 24/7, 365 days per year. The securities that are traded are called currency pairs, which is represented by an exchange rate that describe the amount of one currency need to purchase another. This market has exploded over the past decade, which has led to the question, what is forex trading.
Forex is Made up of Currency Pairs
The forex market is made up of global currency pairs. The pairs that provide the greatest liquidity and have the most volume are major currency pairs. A major currency pair includes the Euro, the British pound, the Australian dollar, the Swiss Franc, the Japanese yen and the Canadian dollar. A pair is considered a major when the base currency is the U.S. dollar. If you trade one of the majors versus another major, such as the Euro versus the Yen, this referred to as a cross currency pair. Additionally, non-major currencies, such as the Swedish Kroner, are referred to as minor currencies. Non-developed countries currencies, such as the Chinese Yuan are called emerging market currencies.
There are a number of ways you can transact a currency trade. Most are done in the over the counter market. Here a broker will provide you with a quote. Brokers will buy a currency pair, such as the EUR/USD at their bid price and sell a currency pair at their offer price. For example, if you see a quote on the EUR/USD for 1.0560/62, the broker will purchase the EUR/USD currency pair at 1.0560 and sell it to you at 1.0562. In the over the counter market, brokers generally do not charge a commission. A broker will generate revenues from the bid/offer spread. You can also transact a currency trade in the futures market, as well as by trading currency ETFs. Additionally, there are contracts for differences which is another was you can take currency risk.
The Spot Rate is the Most Common Exchange Rate
The exchange rate for the most active price is call the spot rate. This means that you agree to deliver your currency to your counterpart in 2-business days. Currency trades, are physically delivered trades, but most brokers will allow you to roll your currency until you decide to take profit or stop loss. So if you trade a spot currency transaction, on the EUR/USD where you buy the Euro and sell the U.S. dollar, you will be expected to place Euro in an account in two business days and deliver the U.S. dollars simultaneously. The rate you would use to trade beyond 2-business days is the forward rate. Here you would add forward points to the spot rate.
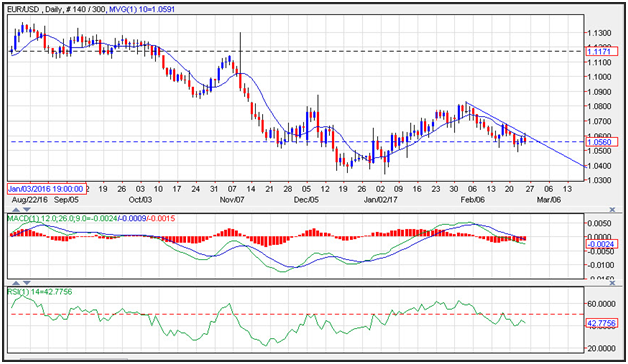
Many traders will use a currency chart to see the history of the exchange rate and attempt to determine the future direction of the currency pair. Technical analysis is a very popular type of study that many traders use to evaluate the forex market.